The 5th "Booking Service Guide for Visits"
- The 5th "Booking Service Guide for Visits">
- Telecommunications Gallery
School Visit Booking - Telecommunications Gallery
This year the booking programs of Telecommunications include the ¡§General Guided Visit¡¨ and ¡§Thematic Guided Visit¡¨. Our facilitators will adjust the content and add hands-on or demonstration parts according to the needs and levels of students. In the ¡§Science Demonstration¡¨, technical devices are used to explain and demonstrate topics related to electricity, light and sound, their scientific theories and applications in daily life. The workshops and electronic circuit courses emphasize hands-on activities in order to supplement what students have learned inside and outside of classrooms. The content will be adjusted according to students¡¦ levels so that they will enjoy and have fun in learning.
General Guided Visit
After the simple introduction by our Facilitators about the exhibitions of Postal/Philately and Telecommunications Galleries and other facilities, visitors can freely experience the most amusing and popular interactive games in the Museum.
Kind reminder:
- Teachers and students are welcome to bring cameras for photo-taking.
- We appreciate very much that teachers and helpers would assist us in taking care of the students during the visit.
- If seats are needed, please inform us upon reservation.
| Item | Audience |
|---|---|
| S1-001 "Basic Guided Visit" | Primary 1 or above, first visit to the Museum |
| S1-002 "Special Guided Visit" | Special guide for disabled students, Primary 1 or above. |
Thematic Guided Visit
A series of related interactive exhibits are displayed and students are encouraged to operate them by themselves. Through the explanation of specific topics and simple science demonstrations, students will have a clearer understanding of the scientific theories and effects concerning the exhibits.
Kind Reminder:
- Some guided visits include additional workshops. If needed, please extend the visiting time of the students accordingly.
- Free visit time for students has been included in the guided visit.
- The content and difficulty of the thematic guided visit will be adjusted to suit the different levels of students.
| Item | Audience | |
|---|---|---|
| Electromagnetism | S3-T01 "Electrostatics" | Primary 4 to Form 3 |
| S3-T02 "Electric Circuit" | Form 1 to 3 | |
| S3-T03 "Electromagnetic Induction" | Form 4 or above | |
| S3-T04 "Alternating Current" | Form 4 or above | |
| Transmission and Broadcasting | S3-T05 "Transmission and Broadcasting" | Primary 4 or above |
| Telegraph and Telephone | S3-T06 "Telegraph and Telephone" | Primary 4 or above |
SCIENCE DEMONSTRATION
Our Facilitators will use specially designed experimental equipment to demonstrate the different science theories and their applications in our daily life.
| Item | Audience |
|---|---|
| S3-D01 "Electrostatics" | Primary 4 or above |
| S3-D02 "Optical Fibers" | Form 1 or above |
| S3-D03 "Laser" | Form 4 or above |
| S3-D04 "Sound and Resonance" | Primary 4 or above |
| S3-D05 "Light and Colours" | Primary 4 or above |
| S3-D06 "Electromagnetism" | Form 1 or above |
| S3-D07 "Direct Current and Alternating Current" | Form 1 or above |
Workshops
The objective of workshops is to let each participant successfully make a simple object or device. This will not only encourage them to learn from the hands-on activities, but also arouse them to learn science and its applications from different perspectives. A variety of workshops of different levels are available for students. After explaining the basic principles, our Facilitators will guide the students to make the related objects.
Kind reminder:
- For our preparation of experiment materials, please make the reservation and confirm the number of participants and the Item number chosen at least 7 days in advance before the visit.
- The content and difficulty of workshops will be adjusted depending on the level of students.
- We appreciate very much that teachers and helpers would assist us in taking care of the students during the workshop.
- The arrangement of free time will depend on the progress of the workshop.
- Some workshops held in the Museum have charges (materials included).
- Workshops can be held at schools. They are charged per student.
Electronic Circuit Courses
The objective of Electronic Circuit Courses is to inspire participants¡¦ thinking and arouse their interests in electronics technology. In addition to one-way teaching, the courses are now going into the direction of interactive learning and mutual study among participants. Hence, they are encouraged to learn and create collectively as a team through making practical teaching aids.
Kind reminder:
- All courses will be conducted in Cantonese, supplemented with English terminology.
- Each course takes 4 weeks, 1 lesson per week, 2.5 hours per lesson.
- From Tuesdays to Saturdays. The detailed timetable has to be compromised between schools or teachers and the Museum.
- Courses can be held in the museum or at schools. They are charged per student (materials included).
- Students who have achieved attendance up to 80% will obtain a certificate after completion of the course.
- The 5th "Booking Service Guide for Visits">
- Telecommunications Gallery

Item: S1-001 "Basic Guided Visit"
Audience: Primary 1 or above, first visit to the Museum
Duration: 60 minutes
Content:
After touring around the main exhibition area, visitors can use their entrance cards to "Design Your Own Stamp" with templates, fly over Macao in the "Flight Simulator", take a "Personal Picture Postcard" and send it to their families and friends, perform the weather forecast in the "Greenscreen Studio", try the Van de Graaff that makes their hair stand, dial the old telephone to call their friends, watch the films at "Mini-Theatre" and hunt the treasure in the "Stamp Lounge".

Item: S1-002 "Special Guided Visit"
Audience: Special guide for disabled students, Primary 1 or above.
Duration: 60 minutes
Content:
A special guide for disabled students. Our Facilitators will design a suitable guided tour upon request and accompany the visitors to "Design Your Own Stamp" with templates, fly over Macao in the "Flight Simulator", take a "Personal Picture Postcard" and send it to their families and friends, perform the weather forecast in the "Greenscreen Studio", dial the old telephone to call their friends, watch the films at "Mini-Theatre".
Interactive option:
"Design Your Own Stamp", "Flight Simulator", "Personal Picture Postcard", "Greenscreen Studio", "Mini-Theatre" or "Handmade Drum".
Electromagnetism
Electromagnetism (electricity and magnetism) is part of classical physics, which analyses the relationships between electric charges, electric field, and magnetic field.

Item: S3-T01 "Electrostatics"
Audience: Primary 4 to Form 3
Duration: 60 minutes
Content:
Our Facilitators will introduce how to induce electrostatics in our daily life. Students can use a piece of fur and a plastic rod to induce static electricity and verify its existence with the electroscope. Besides, through the operation of the Van de Graaff generator that generates high voltage static electricity, students will learn how lightning happens. Students can even touch the metal sphere of the generator with their hands. The electric charges accumulated on the sphere will be carried up to the surface of human body. Since like charges repel each other, their hair will stand up.
Interactive opion:
Free visit or additional 60-minute workshop "Electroscope - I" (Primary: S3-W01); "Electroscope - II" (Secondary: S3-W14).
Electromagnetism
Electromagnetism (electricity and magnetism) is part of classical physics, which analyses the relationships between electric charges, electric field, and magnetic field.

Item: S3-T02 "Electric Circuit"
Audience: Form 1 to 3
Duration: 60 minutes
Content:
Our Facilitators will introduce the components of a basic serial / parallel circuit, their characteristics, differences, advantages, disadvantages, and applications in our daily lives. Students will be invited to use the components to connect a simple circuit and use meters to measure the current and voltage of the circuit. Students can learn about conductors and insulators, the principle and application of voltage divider, the usage of charging and discharging of a capacitor in a direct current circuit through a series of small experiments.
Interactive opion:
Free visit or select 1 additional 60-minute workshop from "Handmade Banknotes Detector" (S3-W04), "Handmade Battery" (S3-W06) or "Soldering Skills" (S3-W07).
Electromagnetism
Electromagnetism (electricity and magnetism) is part of classical physics, which analyses the relationships between electric charges, electric field, and magnetic field.
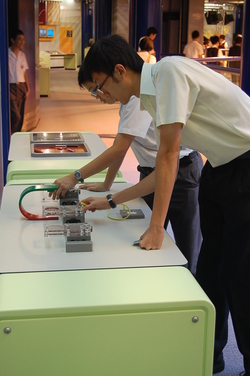
Item: S3-T03 "Electromagnetic Induction"
Audience: Form 4 or above
Duration: 60 minutes
Content:
We shall use a container filled with oil and iron powder to show the magnetic field of magnets. Electromagnetic induction is also shown by flowing current in a solenoid, or by moving coils in a static magnetic field. Besides, an electric generator is provided, with which visitors can feel the magnetic force induced by the electromagnet that are connected to the generator. In addition, an amusing exhibit will show the repellent force between two magnetic fields according to the Lenz's Law.
Interactive opion:
Free visit or select 1 additional 90-minute workshop from "Electromagnet" (S3-W05), "Electromagnetic Swing" (S3-W08) or "Electric Bell" (S3-W10).
Electromagnetism
Electromagnetism (electricity and magnetism) is part of classical physics, which analyses the relationships between electric charges, electric field, and magnetic field.

Item: S3-T04 "Alternating Current"
Audience: Form 4 or above
Duration: 60 minutes
Content:
Students can operate interactive exhibits to learn the structures, types and output of electric generators; to understand the principle of a transformer and the relationship between the number of coils and voltage in a transformer; and to compare the power loss of transmission lines while using high/low voltage for the transmission of electricity and the reason of using high voltage power lines. In addition, students can learn the phenomenon of phase shift, resonance of an A.C. circuit caused by capacitors and inductors as well as the power control circuit and its applications. If there is time available, the principle of charging and discharging of a capacitor, the effect of an inductor in a circuit, and the reactance of capacitors and inductors in A.C. circuit will also be introduced.
Interactive opion: Free visit
Transmission and Broadcasting
Transmission plays an indispensable role in human communication. Until now, there are many different types of transmission and you may see their importance in our daily life. In addition, message needs to be processed before and after transmission, e.g. the composition technique widely used in TV studio to compose different sources of image, processing and saving formats of audio and video information, etc.

Item: S3-T05 "Transmission and Broadcasting"
Audience: Primary 4 or above
Duration: 60 minutes
Content:
We shall briefly introduce the different types and functions of wired and wireless transmission, and demonstrate the application of optical fibers for transmission with several interactive exhibits. Besides, a TV studio is presented to show the composition technique that is widely used to compose different sources of image. Students will learn why the background of the picture can be removed. If time is available, students can explore the information processing area to know different kinds of saving formats of audio and video files.
Interactive opion:
Free visit or additional 60-minute workshop "Optical Fibers DIY" (S3-W02).
Telegraph and Telephone
Telegraph is one of the earliest equipment of long-distance communication. It uses current (cable) or electromagnetic waves (wireless) as the carrier to transmit messages through a coding and decoding process. On the other hand, telephone is the equipment that uses electrical signals to implement the duplex audio communication. Both of them play important roles in the history of communication.

Item: S3-T06 "Telegraph and Telephone"
Audience: Primary 4 or above
Duration: 60 minutes
Content:
Our Facilitators will introduce how to operate telegraph and teletype machines and explain the development, structure, principle and operation of telephone. Demonstration will be conducted to let students understand the functions of telegraph devices, telephones and telephone switching systems.
Interactive opion:
Free visit or additional 60-minute workshop "Handmade Telegraph" (S3-W03).



Item: S3-D01 "Electrostatics"
Audience: Primary 4 or above
Duration: 40 minutes
Content:
In the cold and dry weather, we can often experience static electricity. When we hold a door handle, open metal cabinet or touch others, we can feel the spark on our fingers, which may sometimes take us by surprise. In fact, how does this phenomenon come about? What is static electricity? Does it cause any harm to us? Actually, static electricity is a common phenomenon in nature. It can be caused by friction, contact or induction. Let's learn ways to avoid static electricity so that we can prevent any danger that it may cause us.
The demonstration will be mainly about the causes of static electricity and its related phenomena, including:
- Cause of static electricity: Demonstrate the production of static electricity in different circumstances: electrification by friction, contact and induction.
- Danger of static electricity: The human body and the environment may carry high voltage static electricity, a few thousand volts or more. The electricity discharged by static electricity may also cause damage to surrounding electronic equipment.
- How to prevent static electricity: Ways to prevent static electricity includes discharging, neutralizing, damping, blocking and earthing.
- Interesting electrostatic phenomena - Electrification by induction experiment: Use a charged rod to deflect a wate column by induction; use a charged rod to make a tin can roll by induction.
- Interesting electrostatic phenomena - Electrostatic discharge experiment: Demonstrate the Wimshurst machine and the Van de Graaff generator.
- Applications of static electricity in our daily life: Applications include photocopying machine, electrostatic precipitator, electrostatic painting, etc.

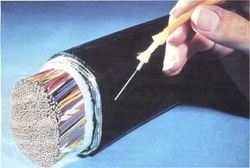
Item: S3-D02 "Optical Fibers"
Audience: Form 1 or above
Duration: 40 minutes
Content:
Optical fiber is an important medium in modern communication. From the Internet to medical equipment, optical fiber is influencing our lives. Recently, telecom operators began providing Fiber to the Home Broadband Service. The access speed is much faster than before and users comment that the speed is incomparable. Optical fiber has suddenly become a hot topic. But what is optical fiber? What are the theories behind it? What benefits has it brought us?
The demonstration will mainly introduce the structure of optical fibers, the theories of message transmission, and compare optical fiber and copper wire, including:
- History of wired communication: Usage of copper wire and its limitations, optical communication at its early stage.
- Operational theories of optical fibers - Characteristics of light: Introduce reflection, refraction and the linear propagation of travel as characteristics of light.
- Operational theories of optical fibers - Optical phenomena of total internal reflection: Use simple tools to demonstrate a light guiding experiment of a water column.
- Operational theories of optical fibers - The birth of modern optical fibers: Introduce the technical difficulties encountered in producing modern optical fibers, the production methods and various types of optical fibers.
- Operational theories of optical fibers - Experiment of sound transmission through optical fibers: The use optical fibers to transmit optical signals.
- Difference between optical fiber and copper wire - Physical properties: Compare the physical properties of optical fibers and copper wire.
- Difference between optical fiber and copper wire - Anti-electromagnetic influence experiment: Use optical fibers and copper wire as the medium of transmission, observe their interference conditions.
- Applications of optical fibers: Endoscope, optical fiber network (data transmission), compare broadband internet access through optical fibers and fixed line (ADSL).
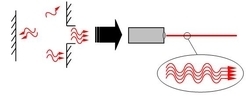


Item: S3-D03 "Laser"
Audience: Form 4 or above
Duration: 40 minutes
Content:
In 1960, a kind of magical light "laser" was born. Since then, laser quite often appears in science fiction movies. Does laser exist only in the future high technological world? Or does it actually exist in our daily life? Let's explore and discover more about this fascinating magical light!
The demonstration concerns the theories and properties of laser, and also its applications, including:
- The theories of the production of laser: Explain the atomic structure of substance, the principle of energy levels and electronic transition, and the production methods of laser.
- Properties of laser - Path: Demonstrate the transmission path of laser.
- Properties of laser - Direction: Comparison between regular light source and laser.
- Properties of laser - Coherence: Explain the coherence of laser.
- Properties of laser - Monochrome: Introduce the monochromatic light transmission of laser.
- Applications of laser - Cutting: Demonstrate cutting of paper, glass, plastic and different materials using a CO2 laser cutter.
- Applications of laser - Communication: Demonstrate and explain the application of optical fibers in communication, and the switching methods between analog and digital signals.
- Applications of laser - Others:Introduce the applications of laser in other areas.
- The safety of laser: Explain the danger of laser and demonstrate with strong laser beams.


Item: S3-D04 "Sound and Resonance"
Audience: Primary 4 or above
Duration: 40 minutes
Content:
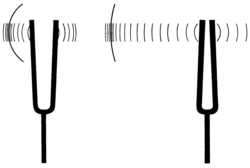
We hear different types of sounds every day. But do we know the theory of sound production? In Physics, what are the theories and phenomena related to sound? Actually, sound is a wave phenomenon caused by the vibration of objects. Vibration will cause different media (including gas, liquid and solid) to produce changes in their density, forming longitudinal waves or what we call "sound waves".
The demonstration concerns the properties of waves and related acoustic phenomena, including:
- Production of sound: Demonstrate how to produce sound by vibration.
- Properties of sound - the three elements of sound(Volume - Amplitude): Introduce the relationship between volume and wave amplitude, and the unit for measuring volume - Decibel (dB).
- Properties of sound - the three elements of sound(Pitch - Frequency): Introduce the relationship between pitch and wave frequency, and the unit for measuring pitch - Hertz (Hz).
- Properties of sound - the three elements of sound(Timbre - Waveform): Introduce the relationship between timbre and waveform, and the overtones produced by different waveforms.
- Transmission of sound: How sound transmitted through mediums.
- Interesting acoustic phenomena - Resonance: Introduce resonance and learn about it from the perspective of Physics and phenomena and experiments related to resonance.
- Interesting acoustic phenomena - Standing wave: Introduce standing wave and its relationship with acoustics, phenomena and experiments related to standing wave.
- Applications related to acoustics in our daily life.


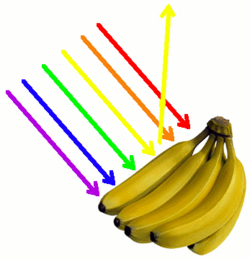
Item: S3-D05 "Light and Colours"
Audience: Primary 4 or above
Duration: 40 minutes
Content:
Sunlight not only gives us light and warmth, but also a lot of beautiful natural phenomena like rainbow, blue sky and sunset glow, etc. But have we ever though about these phenomena are related to the magical effects of light? Light enables us to see our colourful world. Colour is actually a visual effect in response to light produced as seen through our eyes, brain and past experiences.
The demonstration is about the properties of light and related phenomena, including:
- Properties of light: Make use of laser to demonstrate the linear propagation of light, reflection and refraction.
- Dispersion phenomena of light - Compare sunlight, white light and laser by observing their refraction properties after passing through a prism.
- Dispersion phenomena of light - Make an artificial rainbow. Observe and analyze the factors that led to the creation of a rainbow.
- Dispersion phenomena of light - Properties of rainbow: Why is it a curve? Why is it always in a high up position? From which angle can we see a rainbow?
- Types of colours: Compare monochromatic light and coloured light; mixing of the colours of light and the origin of the three primary colours. Use different colour lights to compose lights of different colours.
- Relationship between colour of objects and light: Explain how the colours of objects are brought about. Compare the different colours of objects under lamps of different colours.
- Applications: 3D glasses, stage effect and filter.
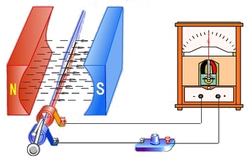
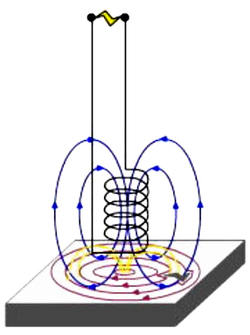
Item: S3-D06 "Electromagnetism"
Audience: Form 1 or above
Duration: 40 minutes
Content:
Since the discovery of the relationship between electricity and magnetism in the early 19th century, a new field of Physics is opened up - Electromagnetism. Since then, we entered to the era of electrification. Following the creation of the power generator, electromagnetism became indispensible to technological advancement. However, how much do you know about electromagnetism? Do you know the intrinsic link between electricity and magnetism? In reality, electricity can create magnetism, and vice-versa. In our daily life, a lot of electrical appliances make use of the theory of electromagnetism.
The demonstration concerns the interaction between electricity and magnetism, and some related phenomena, including:
- Introduce the majors topics of electromagnetism: Basic properties of electromagnetism
- Electricity generates magnetism: How is the electromagnetic field produced? Observe the magnetic effect of electric current produced by energized conductors. Make use of the right-handed screw rule to judge the direction of electromagnetic field.
- Magnetism generates electricity: Let's see how electric current is produced by a coil of changing magnetic field. How to make use of the electromagnetic induction phenomenon for human power generation.
- Mutual induction: Based on the theory of electromagnetic interaction, process energy transmission using two unconnected coils. Let's see how the magical wireless power can light up a lamp without battery!
- Lenz's Law: Observe how the induced current will cause hindering movement to the magnetic field under the magnetism generating electricity phenomenon. Use of the Lenz's Law to find out the direction of electric current produced by the magnetism generating electricity phenomenon.
- Eddy Current: Introduce the formation process of eddy current and its applications, and analyze some related interesting experiments.
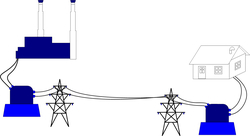
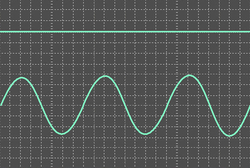
Item: S3-D01 "Direct Current and Alternating Current"
Audience: Form 1 or above
Duration: 40 minutes
Content:
Electricity is indispensable to our modern day life. Whether it is entertainment or machinery for industrial production, electricity is used. What is direct current? What is alternating current? How much do you know about electricity? Join this demonstration and recharge your knowledge database on electricity!
The demonstration concerns the theories and properties of direct current, production and transmission process of alternating current, including:
- Direct current - Basic knowledge: Introduce the definition, properties and applications of direct current, learn about the relationship between electrons movement and electrical energy transmission in the electric circuit.
- Direct current - Joule's Law: Demonstrate the thermal effects of electric current and Joule's Law.
- Direct current - Reasons for choosing direct current: Summarize the advantage and disadvantage of two kinds of electricity in terms of transmission, application and loss.
- Alternating current - Journey of alternating current: Introduce direct current in terms of its process from its production at the power station to its distribution to different districts.
- Alternating current - Learning about transformer: Show an actual transformer and explain its theory and applications.
- Alternating current - Knowing about the electricity supply of Macao: Explain the electricity transmission system and distribution of electrical substations in Macao.
- Alternating current - Secrets in our electricity bill: Explain the different charges on the electricity bill and how to calculate the bill.
- Alternating current - Have a look at direct current and alternating current: Use the oscilloscope to observe direct current and alternating current.

Item: S3-W01 "Electroscope - I"
Audience: Primary 4 to 6
Duration: 60 minutes
Content:
When we rub a plastic ruler, balloon or similar kind of objects against a piece of velvet cloth, it can attract scraps of paper with the static electricity produced. But how can we know if an object carries static electricity? Let's make an electroscope with simple materials to learn more about the basic theory of static electricity.
Charge:
Held in the museum - Free of charge. At schools - MOP30.00 per student.

Item: S3-W02 "Optical Fibers DIY"
Audience: Primary 4 to Form 3
Duration: 60 minutes
Content:
Can you imagine how optical fibers will influence our present and future life? Let us make a simple optical fiber souvenir in order to understand the characteristics, basic transmission theory and its applications in our daily lives.
Charge:
Held in the museum - Free of charge. At schools - MOP30.00 per student.
Item: S3-W03 "Handmade Telegraph"
Audience: Primary 4 to Form 3
Duration: 60 minutes
Content:
Telegraph is one of the earliest equipment for long-distance communication in the history of mankind. It transmits messages with codes through an electrical medium. Following the development of new communication technologies, telegraph is no longer used today but its basic theory is still worth learning. Students can make a telegraph device based on series circuit and bring it home after the workshop.
Charge:
Held in the museum - Free of charge. At schools - MOP30.00 per student.

Item: S3-W04 "Handmade Banknotes Detector"
Audience: Form 1 to 3
Duration: 60 minutes
Content:
Banknote is something that we use or touch every day. How can we identify a fake banknote? In this workshop, students can construct, a low cost, a direct current banknote detector with a simple parallel circuit.
Charge:
Held in the museum - Free of charge. At schools - MOP30.00 per student.

Item: S3-W05 "Electromagnet"
Audience: Primary 4 or above
Duration: 60 minutes
Content:
Everyone should know or at least has heard about magnets since we use them frequently in our daily lives. We might have probably heard about the term "magnetic field", but we may not know why electricity can induce magnetism. This workshop will introduce different types of electromagnets and participants can even make a real electromagnet apart from learning the basic principles of magnetic field.
Charge:
Held in the museum - Free of charge. At schools - MOP30.00 per student.

Item: S3-W06 "Handmade Battery"
Audience: Primary 4 or above
Duration: 60 minutes
Content:
Can coins generate electricity? Yes, we can use coins to make a battery! The coins can still be used as regular money afterwards. What a good idea to protect our environment! Students are requested to bring 10 coins of the same size (MOP 0.50 or 1.00) to the workshop because we will use them to reproduce the first battery "Volta Battery" in the world. Let us learn the basic construction of a battery, the principles of electricity generation and the measurement skills.
Charge:
Held in the museum - Free of charge. At schools - MOP30.00 per student.
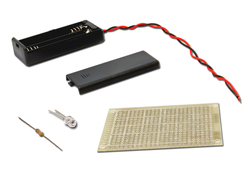
Item: S3-W07 "Soldering Skills"
Audience: Form 1 or above
Duration: 60 minutes
Content:
A lot of electronic devices are assembled with different electric components. The soldering quality of these components will largely affect their performance. In this workshop, participants will learn by practical operation and master the basic soldering skills.
Charge:
Held in the museum - Free of charge. At schools - MOP30.00 per student.

Item: S3-W08 "Electromagnetic Swing"
Audience: Form 3 or above
Duration: 60 minutes
Content:
Have you ever seen any swing moving without wind or anyone pushing it? In fact, we can produce this swing effect by applying the basic theory of electromagnetism. The objective of this workshop is to explain the principles of electromagnetism. Students can apply their knowledge from the textbooks and make a simple electromagnetic swing.
Charge:
Held in the museum - Free of charge. At schools - MOP30.00 per student.
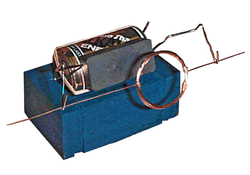
Item: S3-W09 "Direct Current Motor"
Audience: Form 4 or above
Duration: 90 minutes
Content:
In our daily lives, we often see a motor installed in a machine. But, how does it work? What is electromagnetic induction? Let's learn more about electricity, magnet and the application of electromagnetic induction through some experiments and construct a DC motor in the workshop.
Charge:
Held in the museum - Free of charge. At schools - MOP30.00 per student.

Item: S3-W10 "Electric Bell"
Audience: Form 4 or above
Duration: 90 minutes
Content:
Have you ever seen the construction of an electric bell? Do you know how an electric bell works? Why can electricity induce magnetism? Let's learn more about electricity, magnet and the application of electromagnetic induction through some experiments and construction of an electric bell in the workshop.
Charge:
Held in the museum - Free of charge. At schools - MOP30.00 per student.

Item: S3-W11 "Secret of Magnet"
Audience: Kindergarten 3 to Primary 3
Duration: 60 minutes
Content:
Magnet is commonly used in our daily life. But how much do you know about its characteristics? Participants will learn about the north and south poles of magnet and magnetic line of force through the games and experiments of our workshops. They will make a unique magnet which will help them to strengthen their impression of magnetic forces.
Charge:
Held in the museum - Free of charge. At schools - MOP30.00 per student.

Item: S3-W12 "Amazing Static Electricity"
Audience: Primary 1 to 6
Duration: 60 minutes
Content:
Students will learn about static electricity through games and experiments that may reinforce their understanding of electricity. They will try rubbing the balloon with different materials in order to differentiate the amount of static electricity produced by different materials. The games will help to strengthen their impression of static electricity.
Charge:
Held in the museum - Free of charge. At schools - MOP30.00 per student.
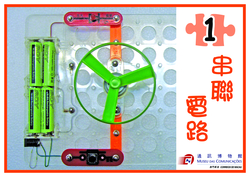
Item: S3-W13 "Labyrinth of Electric Circuits"
Audience: Primary 1 to 6
Duration: 60 minutes
Content:
The workshop will introduce about the characteristics of conductors and insulators, circuits and their compositions. Students will use circuits puzzle to connect different parts to compose a closed circuit. They can also strengthen their knowledge of closed circuit through the game of current rod.
Charge:
Held in the museum - Free of charge. At schools - MOP30.00 per student.

Item: S3-W14 "Electroscope - II"
Audience: Form 1 or above
Duration: 60 minutes
Content:
When we rub a plastic ruler, balloon or similar kind of objects against a piece of velvet cloth, it can attract scraps of paper with the static electricity produced. But how can we know if an object carries static electricity? Is it "+" or "-" charge? Let's use FET, which is a semi-conductor that controls electric current through the electric field, to see how it is affected by electrostatic field and, hence, learn the basic theory of static electricity.
Charge:
Held in the museum - Free of charge. At schools - MOP30.00 per student.
Note:
Soldering-iron is used, please pay attention to safety.

Item: S3-W15 "The Fun of Sound & Wind Music"
Audience: Primary 4 to 6
Duration: 60 minutes
Content:
Sound will be produced when the air inside a straw vibrates. How can we make a pan flute that produces better sounds, and how to tune it? Now let's learn the theories of producing sound by air vibration and air column resonance.
Charge:
Held in the museum - Free of charge. At schools - MOP30.00 per student.

Item: S3-W16 "Simple Periscope"
Audience: Primary 1 to 4
Duration: 60 minutes
Content:
Based on the principle of light reflection, the periscopes used in submarines are made for observing the water surface from the submarine. Let's make a periscope with simple materials to understand its structure and principle.
Charge:
Held in the museum - Free of charge. At schools - MOP30.00 per student.


Item: S3-W17 "Simple Telescope"
Audience: Primary 3 to 6
Duration: 60 minutes
Content:
How does a telescope bring distant objects to the front of our eyes? Let's make a simple telescope (the simplest one can be made only by 2 mirrors!) and understand how the principles of reflection and refraction are applied in telescopes.
Charge:
Held in the museum - Free of charge. At schools - MOP30.00 per student.


Item: S3-W18 "Bling Bling Kaleidoscope"
Audience: Primary 5 to 6
Duration: 60 minutes
Content:
Why does the pattern inside a kaleidoscope change when we slightly rotate it? Kaleidoscope is actually an optical toy that consists of three mirrors inside the tube. With light reflection, the colored bits of glasses inside the tube will form different beautiful and colorful patterns.
Charge:
Held in the museum - Free of charge. At schools - MOP30.00 per student.
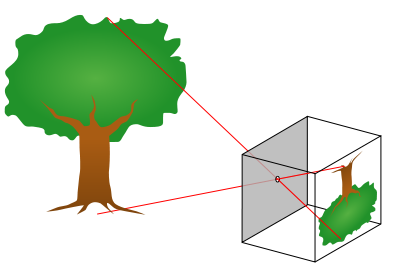
Item: S3-W19 "Pinhole Camera"
Audience: Primary 6 to Form 2
Duration: 60 minutes
Content:
Do you know how a camera works? Actually the principles of most cameras work are similar. Let's make a simple pinhole camera to see how an image is projected by light rays and, hence, the principles of a camera.
Charge:
Held in the museum - Free of charge. At schools - MOP30.00 per student.

Item: S3-W20 "Control of Direct Current Motor"
Audience: Form 1 or above
Duration: 60minutes
Content:
Direct current (DC) motor is one of common electro-mechanic elements in our daily lives, it is easily found in mobile phones, tools, etc. Secondary students can learn the operational theories of a DC and how to apply a DC motor in terms of position control (CW/CCW) and velocity control, etc.
Charge:
Held in the Museum - MOP20.00 per student. At schools - MOP30.00 per student.
Item: S3-W21 "Component Commando"
Audience: Primary 4 or above
Duration: 2 lessons, 90 minutes/lesson (Or 1 lesson of 180 minutes)
Content:
A variety of electronic components are used in different electronic devices. Do you know their names and purposes? Through assembly robots with different electronic components, participants will learn their names and purposes.
Charge:
Held in the museum - MOP 30.00 per student. At schools - MOP 50.00 per student.
Note:
Participants of Form 1 or above will use soldering-irons. Please pay attention to safety.

Item: S3-W22 "Fun Group Game"
Audience: Primary 4 or above
Duration: within 2.5 hours
Content:
Participants will learn to use certain kinds of communication tools and methods through games. They will be divided into groups to contest or complete some tasks. The objective is to let them know the importance of communication and cooperation with their teammates in a new environment.
Charge:
Held in the museum - Free of charge. On-site service at schools is not provided.
Note:
For the purpose of group division, the number of participants should not be more than 35. The venue of the activities includes both the indoor and outdoor areas of the Museum. Please put on casual or sports wear.
Item: S3-E01 "Introduction to Circuit and Soldering"
Audience: Form 3 or above
Duration: 4 weeks, 10 hours
Content:
Switches, resistors, capacitors, diodes, transistors and integrated circuits are the most common electronic circuit components. These components are applied in household appliances and industrial devices to perform different functions. Before understanding the usage of these components, we need to understand two basic connection methods - series & parallel. During this course, through simple calculation and use of a multifunctional meter, students will learn the difference between these two types of connection and also soldering technique.
Charge:
Held in the museum - MOP50.00 per student. At school - MOP70.00 per student.
Outline:
Lesson 1 - Knowing the circuits and electronic components.
Lesson 2 - Testing the circuit, components and voltage with multifunctional meter. Resistors and capacitors connected in series and parallel circuits; Ohm's law.
Lesson 3 - Introduction to diodes, transistors and soldering techniques.
Lesson 4 - Soldering training.

Item: S3-E02 "Application of Photodiode - Photosensitive Mechanical Beetle"
Audience: Form 3 or above, completion of S3-E01 is recommended
Duration: 4 weeks, 10 hours
Content:
Students will be introduced about LEDs, photodiodes, NPN type transistors, DC motor and their application as a whole. They will use the above-mentioned components to build a photosensitive mechanical beetle, which follows light to guide its way.
LED is a semiconductor component widespread and popular due to its long service life, versatile color changing ability and low power consumption. Applications of LEDs are so diversified in fabrication of indicator light, display boards and lighting that they show many advantages over traditional light sources, such as lower energy consumption, longer lifetime, improved robustness, smaller size and faster switching.
A photodiode is a typical photo detector which is capable of converting light into either current or voltage, depending upon the mode of operation. It is usually found in automatic control system.
Transistor is a semiconductor device commonly used to amplify or switch electronic signals. The NPN transistor used in this course is like a switch where the input voltage is applied to change the output current. Unlike other mechanical switches, transistor can use electrical signals to control the switch "on" and "off" with high speed.
Charge:
Held in the museum - MOP50.00 per student. At school - MOP70.00 per student.
Outline:
Lesson 1 - Review of electronic components and soldering technique.
Lesson 2 - Introduction to LED, photodiode, NPN transistor and DC motor.
Lesson 3 - Constructing a photosensitive mechanical beetle.
Lesson 4 - Constructing a photosensitive mechanical beetle.
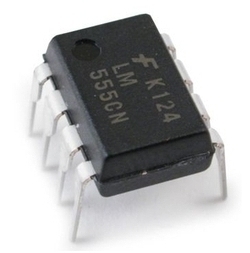

Item: S3-E03 "Introduction to 555 Timer and Its Applications"
Audience: Form 4 or above
Duration: 4 weeks, 10 hours
Content:
555 timer gets its name from the three 5 kΩ resistors connected inside its circuit. It is an integrated circuit combined with both analog and digital functions. When it is connected to other resistors and capacitors, it performs the function like an oscillating circuit. 555 timer is widely used in household appliances, measuring instruments, automation and electronic toys. This course aims at introducing IC 555 timer and its integration, especially major applications of monostable and astable oscillating circuits. Students will practice soldering circuit boards to construct simple flash and on/off lighting circuits.
Charge:
Held in the museum - MOP50.00 per student. At school - MOP70.00 per student.
Outline:
Lesson 1 - Introduction to 555 timer and astable oscillating circuit.
Lesson 2 - Construction of 555 flash lighting circuit.
Lesson 3 - 555 monostable oscillating circuit.
Lesson 4 - Construction of 555 on/off lighting circuit.

Item: S3-E04 "Construction of Electronic Piano with IC 555"
Audience: Form 4 or above, completion of S3-E03 is recommended
Duration: 4 weeks, 10 hours
Content:
Sound is produced by vibration and variations in the frequency of vibration per second will produce different tones. A 555 astable oscillating circuit can be applied in an electronic piano to generate different tones. This means that the circuit will drive different combinations of resistors and capacitors to produce different frequencies of oscillation, like controlling the flashing speed of a LED by the flash circuit.
Participants of this course can apply their theoretical knowledge in practice to make an electronic piano by selecting and calculating frequency and resistance values, and soldering the circuit board of the device.
Charge:
Held in the museum - MOP50.00 per student. At school - MOP70.00 per student.
Outline:
Lesson 1 - Fundamentals of IC 555 and frequency of music.
Lesson 2 - Principles of electronic piano circuit with IC 555.
Lesson 3 - Construction of electronic piano circuit with IC 555.
Lesson 4 - Construction of electronic piano circuit with IC 555.
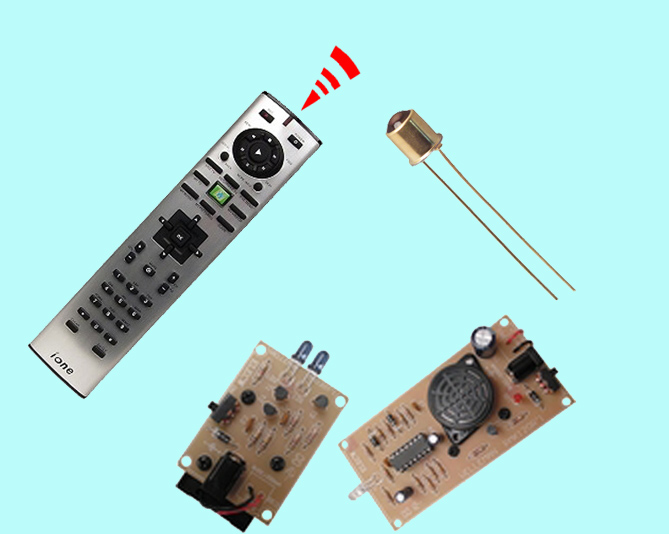
Item: S3-E05 "Application of Infrared Communication Technology"
Audience: Form 4 or above
Duration: 4 weeks, 10 hours
Content:
Infrared (IR) is an electromagnetic wave whose wavelength is longer than visible light but shorter than microwave. Since no physical connection and no complicated components are needed for IR communications, the cost of transmission is lower. This explains why it has become a common technology applied in portable computer, mobile phones and other transmission equipment for data transfer. It is also used in the remote control of TV, air-conditioner and other household appliances.
This course allows students to experience the applications of infrared in our daily life by making gadgets by themselves. Participants will produce an infrared receiver that connects to the computer and use an ordinary household remote control to substitute the operation of the mouse or keyboard of the computer.
Charge:
Held in the museum - MOP50.00 per student. This course cannot be done at schools because oscilloscopes are needed.
Outline:
Lesson 1 - Introduction to 555 monostable oscillating circuit.
Lesson 2 - Introduction to infrared communication technology and making the receiver.
Lesson 3 - Making the circuit of receiver.
Lesson 4 - Introducing the WinLIRC and making a PC remote control.

Item: S3-E06 "Introduction to 4017 Decade Counter and Its Applications"
Audience: Form 4 or above, completion of S3-E03 is recommended
Duration: 4 weeks, 10 hours
Content:
The IC 4017 is a decade counter that is widely used like the 555 timer. It is usually found in counting circuits, electronic switches, flash lighting and electronic games. The 555 timer and 4017 counter can be combined in circuits to perform different functions.
This course will allow students to acquire knowledge of IC 4017 from its integration and applications. Students will use a hybrid circuit of 555 timer and 4017 counter to make an electronic device - Fortune Wheel and solder the circuit board of the device.
Charge:
Held in the museum - MOP50.00 per student. At school - MOP70.00 per student.
Outline:
Lesson 1 - Fundamentals of IC 4017 and its applications.
Lesson 2 - Circuit with IC 4017 and IC 555 for the Fortune Wheel.
Lesson 3 - Making the circuit of Fortune Wheel.
Lesson 4 - Making the circuit of Fortune Wheel.
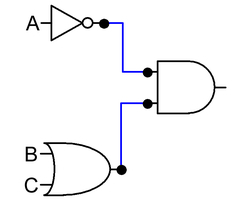
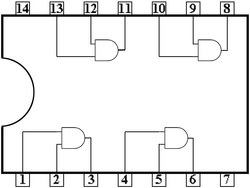
Item: S3-E07 "Principles of Digital Logic Circuits"
Audience: Form 4 or above, completion of S3-E01 is recommended.
Duration: 4 weeks, 10 hours
Content:
Integrated circuits of AND, NAND and OR gates are not only used for electronic devices, but also the basic elements of computer operation units. IC 7408, 7432 and 7404 for AND, NAND and OR gates are commonly applied in basic digital logic circuits. Students will learn the principles of digital logic circuits from hands-on practice of making the Rock-Paper-Scissors game.
Charge:
Held in the museum - MOP50.00 per student. At school - MOP70.00 per student.
Outline:
Lesson 1 - Introduction to digital logic circuits and truth table.
Lesson 2 - Introduction to IC 7408, 7432 and 7404.
Lesson 3 - Construction of the Rock-Paper-Scissors game.
Lesson 4 - Construction of the Rock-Paper-Scissors game.

Item: S3-E08 "Application of Operational Amplifiers - Hearbeat Sensor"
Audience: Form 4 or above, completion of S3-E01 is recommended.
Duration: 4 weeks, 10 hours
Content:
The infrared rays from an Infrared LED can pass through human skin. When the heart beats, blood flows through the blood vessels inside our fingers. At the same time, the infrared rays received by the photodiode also changes, which results in a weak electric signal. When this electric signal is magnified by an operational amplifier, which in turn lights up an LED, we can observe the heart rate. In this course, participants will learn how to make a simple Heart Rate Monitor and learn about the application of operational amplifier in our daily life.
Charge:
Held in the museum - MOP70.00 per student. This course cannot be done at schools because oscilloscopes are needed.
Outline:
Lesson 1 - Basic principles of electric circuits and heart rate monitors.
Lesson 2 - Basic principles of operational amplifiers.
Lesson 3 - Production of heart rate monitor.
Lesson 4 - Production of heart rate monitor.

Item: S3-E09 "Production of Wind Power Generator"
Audience: Form 1 or above
Duration: 4 weeks, 10 hours
Content:
Wind power is a new kind of unpolluted and renewable energy that has a huge potential for development. Human beings can make use of windmills to convert the energy of wind into rotational motions which will in turn drive the power generator to produce electricity.
In this course, students apply the Faraday's Law of Induction to make a simple wind power generator which will be tested with a light-emitting diode.
Charge:
Held in the museum - MOP50.00 per student.
Outline:
Lesson 1 - Principles and structure of the wind power generator.
Lesson 2 - Production of the main body of the wind power generator (coils) and the blade.
Lesson 3 - Assembly of the body of the wind power generator.
Lesson 4 - Integration and testing.

Item: S3-E10 "Production of Teaching Aids - Van de Graaff Generator"
Audience: Form 4 or above
Duration: 4 weeks, 10 hours
Content:
The Van de Graaff Generator makes use of friction to produce electricity and accumulates a lot of electric charges in its metallic ball. These electric charges can produce high voltage which can be used to demonstrate many interesting phenomena of static electricity. For instance, it can cause the hair to stand up, attract paper scraps, produce electric sparks, etc. We encourage participants to use recycled materials to make a Van de Graaff Generator to understand the characteristics of static electricity.
Charge:
Held in the museum - MOP80.00 per group (2 persons/group).
Outline:
Lesson 1 - Introduction of the generation of static electricity and principles of the Van de Graaff Generator, discussion about the device's size and suitable materials for production.
Lesson 2 - Production of the Van de Graaff Generator.
Lesson 3 - Production of the Van de Graaff Generator.
Lesson 4 - Testing and improvement, participants' sharing on difficulties encountered and solutions of problems during the production process.
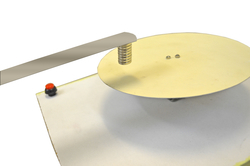
Item: S3-E11 "Production of Teaching Aids - Electromagnetism"
Audience: Form 4 or above
Duration: 4 weeks, 10 hours
Content:
Participants will learn to make teaching aids related to electromagnetism, for example, electromagnetic brakes. Apart from frictional belt brakes, what are other ways to stop a car? Are there any contactless brakes? In fact, we can apply the theory of electromagnetic induction to create a braking effect. Through making a teaching aid, participants will understand the theory and practical application of electromagnetic induction in terms of an electromagnetic brake.
Charge:
Held in the museum - MOP80.00 per group (2 persons/group).
Outline:
Lesson 1 - Introduction of theories, discussion about the device's size and suitable materials for the production.
Lesson 2 - Production of an electromagnetic brake model.
Lesson 3 - Production of an electromagnetic brake model.
Lesson 4 - Testing and improvement, participants' sharing on difficulties encountered and solutions of problems during the production process.
